PDAC
Recently, I read a new paper about pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), published in nature communication.
It mainly studies human PDAC and applies scRNA sequencing on freshly collected human PDAC samples before or after chemotherapy. The abstract has three main results: 1) They find a heterogeneous mixture of basal and classical cancer cell subtypes, along with distinct cancer-associated fibroblast and macrophage subpopulations. 2) Classical and basal-like cancer cells exhibit similar transcriptional responses to chemotherapy and do not demonstrate a shift towards a basal-like transcriptional program among treated samples. 3) Ligand-receptors decrease interactions in treated samples, particularly between TIGIT on CD8 + T cells and its receptor on cancer cells, and identify TIGIT as the significant inhibitory checkpoint molecule of CD8 + T cells.
Let us see how they analyze the three results.
One、How to judge the cut-off between basal and classical cancer cell subtypes?
Here, the researchers found there is no difference between upon conditions.
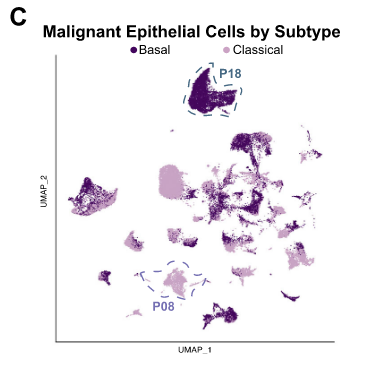
All samples but one were comprised of a mixture of basal and classical cancer cells in varying proportions.
Although we did not observe this specific intermediate state gene signature (the number of samples in each dataset may limit the generalizability of such a signature), we did discover cancer cells in numerous patient samples that expressed both basal and classical histological markers to varying degrees.
Two 、How to detect Classical and basal-like cancer cells exhibiting similar transcriptional responses?
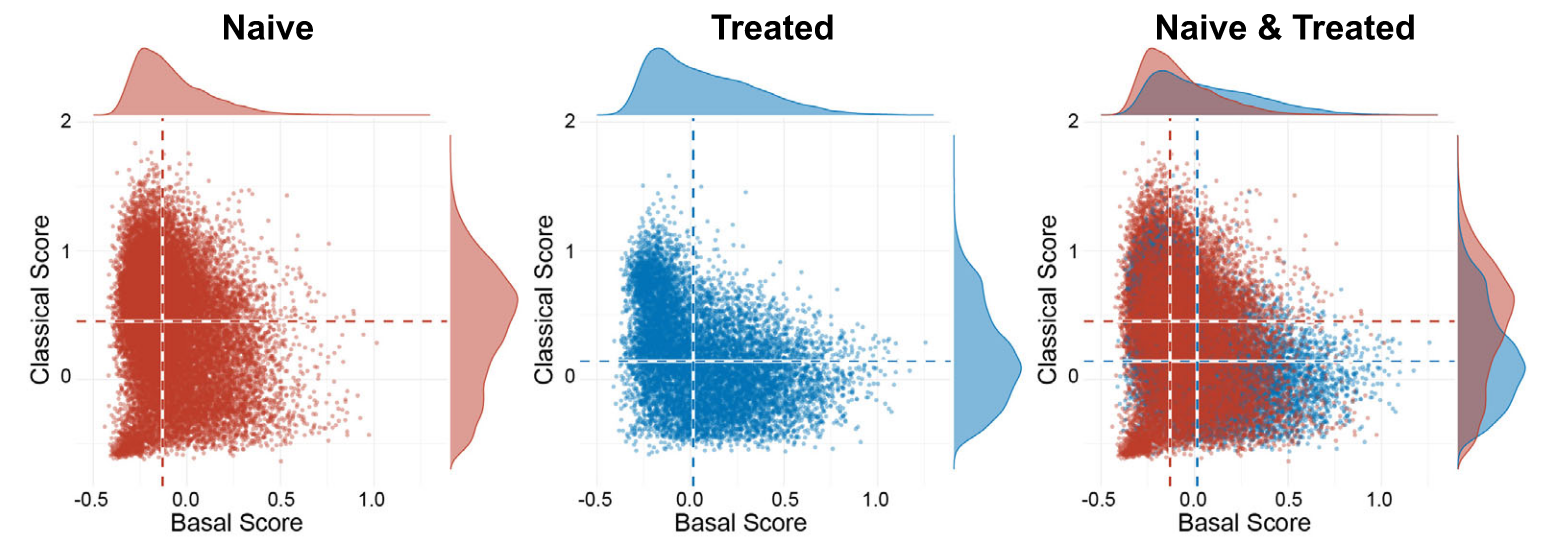
Through gene sets score, they found two groups' cells are mostly overlapped.
Three、How to ensure ligand-receptors decreased interactions in treated samples?
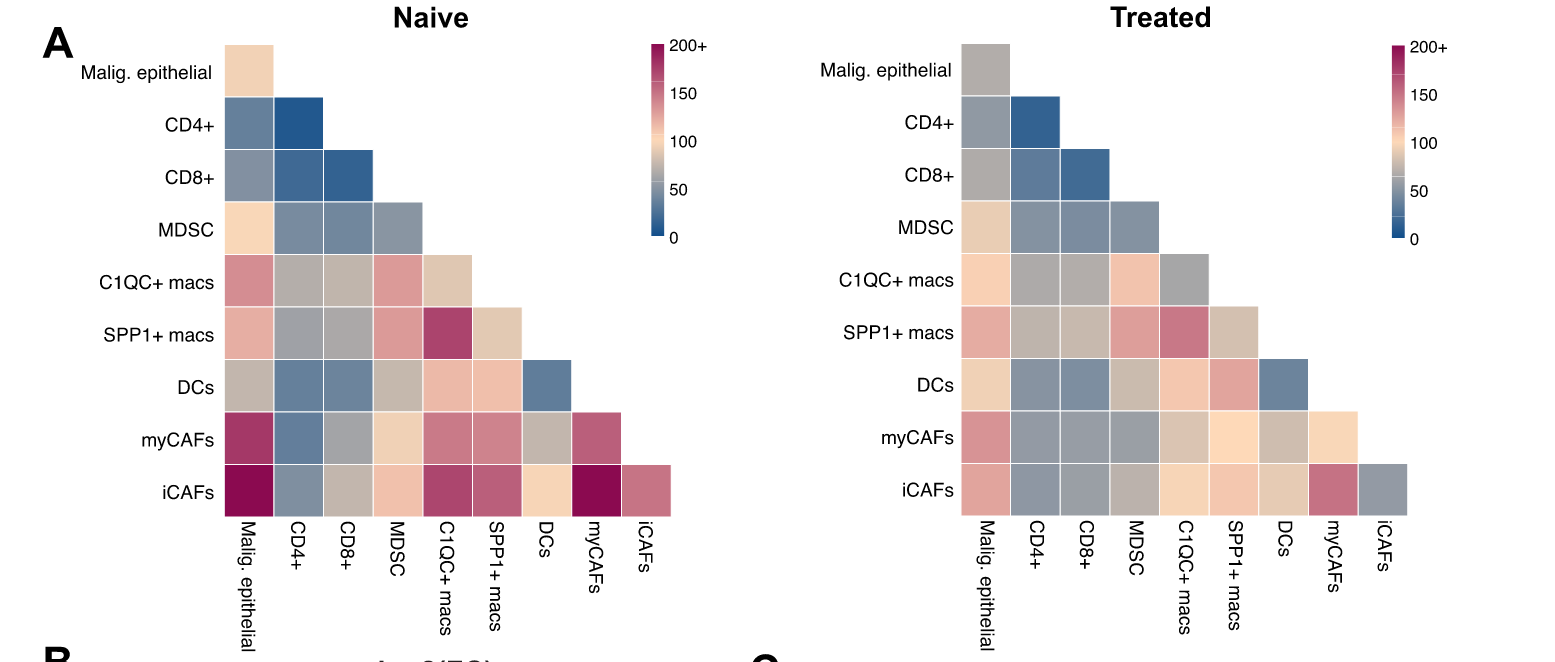
They employed CellPhoneDB to infer potential ligand-receptor interactions (LRIs) between malignant epithelial cells, TAM and CAF subpopulations, CD8 +and CD4 + T cells, MDSCs, and DCs in naïve and treated samples and found a general decrease of cell-cell interactions in the chemotherapy-treated group by fold change value.